Creating an Impact Strategy: A Step-by-Step User Guide
We use a logic model is a visual representation of the relationships between a program or project's resources, activities, outputs, and outcomes. However, the model has much more reach as it focuses on data, surveys, and data binding. Our ultimate goal is to provide a flexible but end-to-impact strategy. It provides a systematic way of illustrating how a program's components contribute to achieving its goals. This user guide will walk you through creating a logic model using the provided example.
Step 1: Create a Project
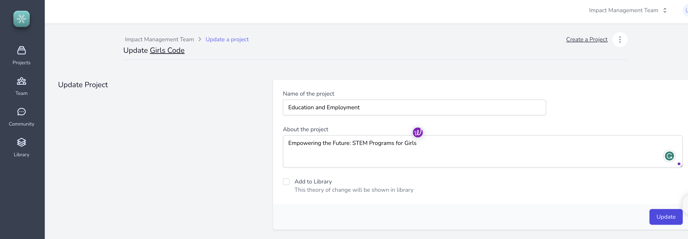
- Start by creating a new project for your logic model. Name the project based on its purpose or focus. In this example, the project is named "Education and Employment."
- About the Project: Empowering the Future: STEM Programs for Girls
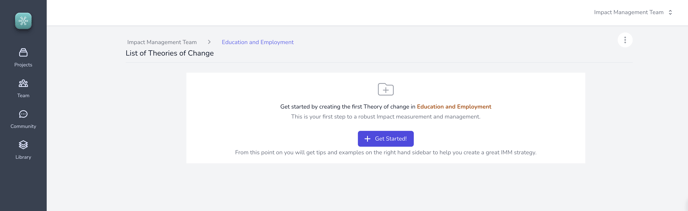
Step 2: Click on New Theory of Change
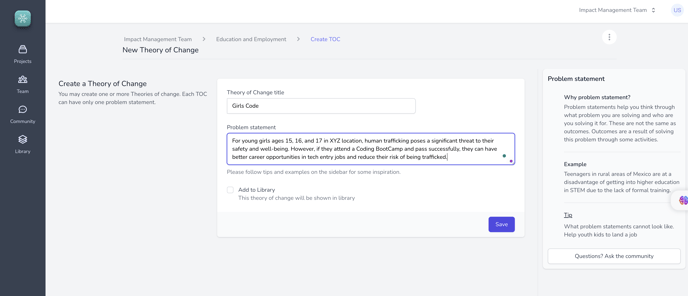
Step 3: Define the Theory of change
- In the "Theory of Change" section, specify the problem statement that your project aims to address.
- For this example, the problem statement is: "For young girls ages 15, 16, and 17 in XYZ location, human trafficking poses a significant threat to their safety and well-being. However, if they attend a Coding BootCamp and pass successfully, they can have better career opportunities in tech entry jobs and reduce their risk of being trafficked."
Step 3: Add Activities
- In the main view, find the button labeled "+ Add Activity" below the problem statement and click on it.
- Define the activities that your program will implement to address the problem.
- For this example, the activity is: "We run an online educational platform where the girls not only learn coding by following the lessons posted on the LMS system but also take tests on technical concepts."
Step 4: Define Activity Metrics
- Add activity metrics that correspond to each activity. These metrics help quantify the program's efforts.
- In this example, the activity metrics are:
- "# number of girls registered in the online platform"
- "# number of technical lessons on the LMS system"
Step 5: Define Outputs and Output Metrics
- Define the outputs that result from the program's activities, and specify the metrics to measure these outputs.
- In this example, the outputs and output metrics are:
- Output: "Girls learn to code and start building applications" Output Metric: "# number of girls that build an app post-course"
- Output: "Girls get jobs in the tech industry after finishing the course" Output Metric: "# Number of girls that finished the course successfully with a passing score on the completion test" Output Metric: "# number of girls that got a job in the tech industry after completing the course."
Step 6: Define Outcomes and Outcome Metrics
- Specify the intended outcomes the program aims to achieve and the metrics to assess these outcomes.
- In this example, the outcomes and outcome metrics are:
- Outcome: "Improving the quality of life of these young girls who otherwise would have been a victim of human trafficking" Outcome Metric: "% of girls who were saved from trafficking and that went on to take a job in the tech industry" Outcome Metric: "% of girls that earn more than the median salary for the position based on the location" Outcome Metric: "% of girls that express satisfaction over the quality of job and their work environment."
Step 7: Utilize the Comment Feature
- Use the comment feature to document your work, provide feedback, and engage with other team members.
Step 8: Save and Review the Logic Model
- Save your logic model and review it to ensure it accurately represents the program's theory of change and the relationships between its components.
Congratulations! You have successfully created a logic model for your program. This visual representation will help you and your stakeholders understand how your program's activities, outputs, and outcomes are connected and how they contribute to achieving your program.
